Consequences of Not Spaying/Neutering
Aside from avoiding unwanted pregnancy, there are many benefits to having your pet spayed or neutered. Behavioral benefits include decreased aggression, decreased urine marking/spaying, and decreased sexual behaviors such as humping. Animals that are spayed or neutered are less likely to roam and less likely to be in fights with other animals.
Additionally, there are many health benefits. Animals that are spayed or neutered early in life are less likely to have mammary cancer and prostate problems. Spayed or neutered animals cannot develop cancers or diseases of the uterus, ovaries, or testicles since these organs are removed during surgery. The following is a collection of pictures of reproductive problems that could be avoided with early spaying/neutering.
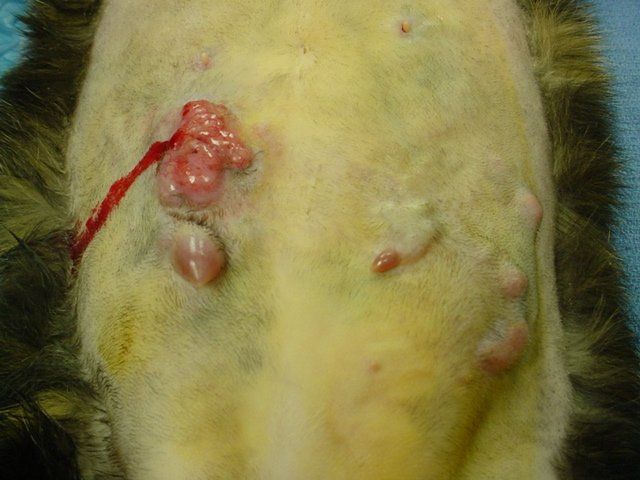
MAMMARY ADENOCARCINOMA (CANCER). Mammary cancers are more common in not-spayed females. Spaying before the first heat cycle dramatically decreases the risk of mammary cancer in dogs/cats when they age. Spaying after a litter of puppies/kittens or after two or more heat cycles is not as protective as spaying early.
This cat has several mammary masses. Some have ruptured and are bleeding. The overall rate of survival for this cat is poor, even with radical surgery, radiation, and/or chemotherapy. Mammary masses should be removed when they are small and first detected as the survival rate is often better if removed early.
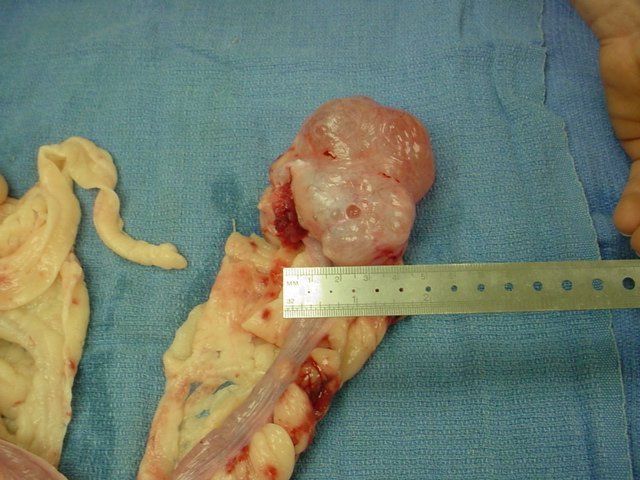
POLYCYSTIC OVARIES. At left is a picture of grossly enlarged and cystic ovaries. They measured approx. 2 x 4 inches in this dog and should have been approx. 1 x 1 inch or smaller. Cystic ovaries can be painful and cause strange or absent heat cycles. In addition, they can rupture and bleed resulting in abdominal pain and infection in some instances.
This dog had bilateral (both sides) polycystic ovaries. She had a painful abdomen, a lack of appetite, and weight loss.
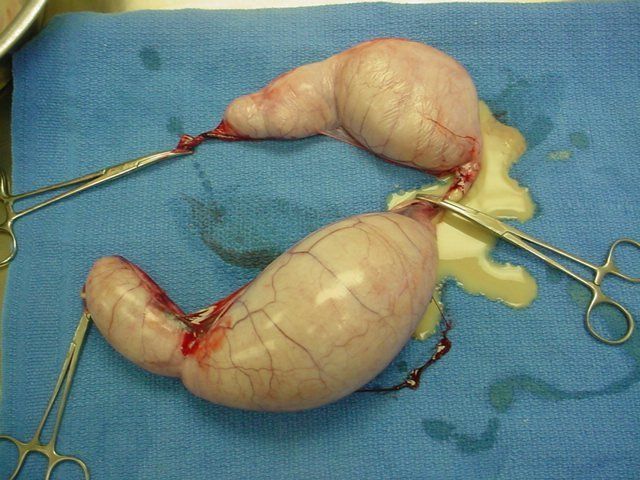
PYOMETRA (UTERINE INFECTION). Intact females can develop a life-threatening uterine infection after their heat cycles. The uterus swells and fills with pus. These infections are often severe and can result in death if not treated aggressively. Signs of a pyometra include vomiting, increased thirst, a painful abdomen, lack of appetite, decreased activity, and a foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
The uterus in this picture is from a cat. Normally, it would be about the width of the tips of the clamps seen in the picture. Pus can be seen draining from the cut end of the uterus.
Other complications of not spaying/neutering include TESTICULAR CANCER, TESTICULAR TORSION, and PROSTATIC DISEASE. Pictures will be added as they become available.
For more information on the benefits of spaying and neutering, click here.


Share On: